Hacking public transport APIs - written by NiXijav on 2018-09-24

Living in Santiago de Compostela or Vigo? Then this post is for you.
If you're usually using public transport, it's useful knowing when your bus is going to arrive. For this reason, I've created a website and a telegram bot.
For Santiago's public transport there are two options. The first one, buscq.com. Aimed for desktop devices, you'll be able to select your desired stop inside each bus line. Currently, it doesn't support searching. You have to know where you're going!

Buscq.com main menu
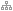
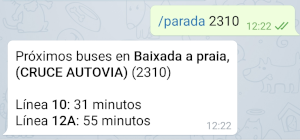
You also have @buscq_bot on Telegram. It only has one command, /parada. As a parameter, either the stop number or stop name are accepted.
Search by stop ID
Search by stop name
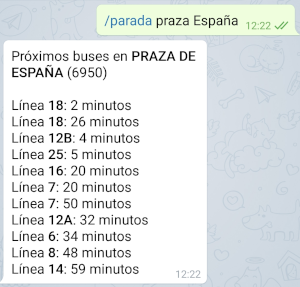
If your name search yields more than a result, a disambiguation message will be shown.
Disambiguation dialog
If you don't know where you are, you can send your current location, and the 10 nearest stops will be returned. You can then use /parada with the name or id.
On the other hand, if you're living in Vigo, there is @vitrasa_bot, also on Telegram. It works just like the Santiago one, but with Vigo data (obviously). It'll return 15 results instead of 10 in disambiguations and nearest stops
Fun fact: there are 580 bus stops in Santiago and 1192 in Vigo.
Source code for buscq and buscq_bot is available here, under the GPLv3Source code for vitrasa_bot is available here, also under the GPLv3
Simplifying the MCP23017 - written by NiXijav on 2016-03-01

Library for the Raspberry Pi written in Python that simplifies the use of the MCP23017, a 16 bit GPIO expander
The MCP23017 is a very useful IC. It provides 16 GPIOs, and it's ideal for expanding the ports of a Raspberry Pi. It even includes pullup resistors for each pin, and all of this using i2c.
You can find the datasheet for this chip here
But all this benefits come at a price. It is not easy to use, or at least, not easy to use initially. The MCP23017 operates entirely based on registers (Page 9 of the datasheet), and depending on which register you are writing to, you'll be able to change the direction of the pins, state, pullups... Also, GPIOs are divided into two different banks, and they are independent from each other.
To simplify this boring register thing, I created a library, in Python, for the Raspberry Pi. Commands are almost the same as the RPi.GPIO ones.
Here is the pinout the library uses:
A very simple code example:
```import mcp23017_lib as MCP
MCP.start(0x26)
MCP.setup(2, MCP.IN, MCP.PUHIGH)
MCP.setup(1, MCP.OUT)
while 1:
if(MCP.input(2)):
MCP.write(1, MCP.HIGH)
else:
MCP.write(1, MCP.LOW)
```
This example will set pin #2 as an input, with the pullup resistor enabled and #1 as an output. When the input goes high, pin #1 will also go high.
You can find the library here. It is licensed under the GPLv3.
If you found this library useful, and/or have suggestions, please let me know in a comment :3
BabbageBot - written by NiXijav on 2015-10-15

BabbageBot is a Python bot for Slack. Modular, easy to use and fun.
BabbageBot is a Python made bot for Slack, the communication tool for teams. The bot provides easy to add and easy to modify commands that can greatly expand the experience of chatting.
It was made with the intention of being modular, enabling anyone that wants to modify it to do the changes very easily. The structure of the bot is:
├── LICENSE
├── main.py
├── modules
│ ├── btc.py
│ ├── calc.py
│ ├── help.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── iss.py
│ ├── list.py
│ ├── ping.py
│ ├── rand.py
│ ├── translate.py
│ ├── weather.py
│ └── wiki.py
└── README.rst
The main.py contains the main methods for connecting to the Slack API through a Websocket. An API key is required. This file also loads the modules/list.py. List.py enumerates all the available modules (aka commands), and main.py uses this list as the message filter. When a string is detected to be in the list, this message gets delivered to the appropriate module. Result is then returned from the specific module and sent back to Slack.
The modules folder, as already said, contains all the modules that can be used by the bot. Each command should have its own file. Not required, but recommended.
For example, calc.py computes any kind of mathematical expression by sending the data to a server and then retrieving the result. Modules like the weather one require an API key. (In this case, from Openweathermap)
Adding a command is pretty simple. Create a .py file with any name in the modules/ folder. Then create the 'execute' function, with an string as a parameter (even if you don't use it). For example, I'll use the file 'wiki.py' (Fetches the Wikipedia). Inside the execute function I have all the necessary code to fetch the relevant Wikipedia article based on the given arguments.
After the code is properly written and working, an entry should be added in modules/list.py. First, importing it (eg, 'import wiki'); and then adding the entry itself in 'commandModules'. In this case I would add ''wiki': wiki'. The first 'wiki' is the keyword the bot will be listening for executing the command specified on the second half, 'wiki'. You could also have ''potato': wiki', and then sending to the bot 'potato Trees' would return the Wikipedia article about trees.
BabbageBot is distributed under the GNU Affero GPL v3 license.
For more information on installing, modifying and redistributing, please visit this GitHub repository: BabbageBot